クラスタリングモジュール#
クラスタリングモジュールの目的#
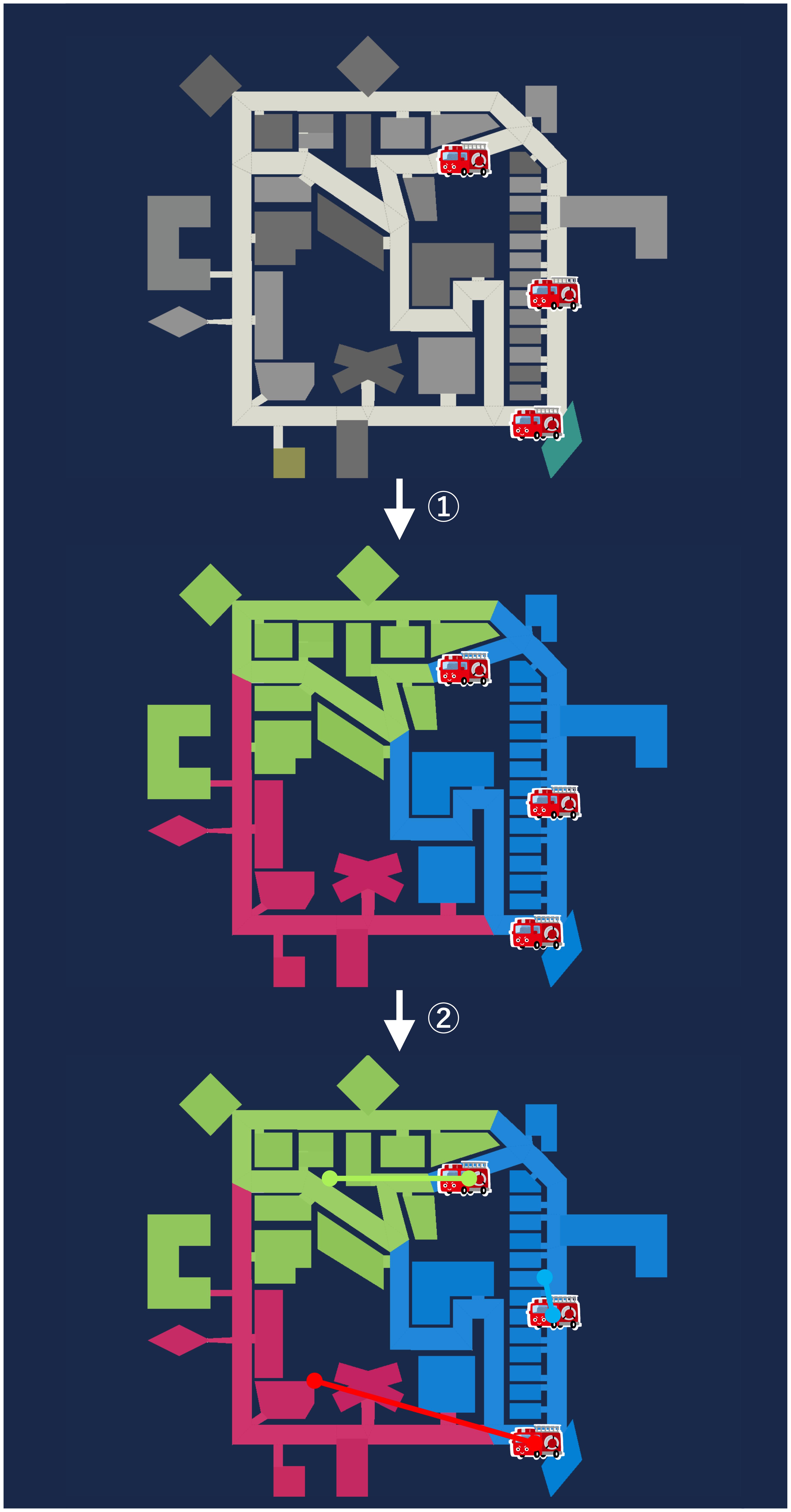
複数のエージェントを動かす場合は、それらのエージェントにどのように協調させるかが重要になります。RRS では多くのチームが、エージェントに各々の担当地域を持たせ役割分担をおこなう協調を取り入れています(他の手段による協調も取り入れています)。担当地域を割り振るためには、地図上のオブジェクトをいくつかのグループに分ける必要があります。このようなグループ分けをしてそれらを管理する場合には、クラスタリングモジュールと呼ばれるモジュールを用います。
本資料では、多くの世界大会参加チームが使用しているアルゴリズムを用いたクラスタリングモジュールの実装をおこないます。
開発するクラスタリングモジュールの概要#
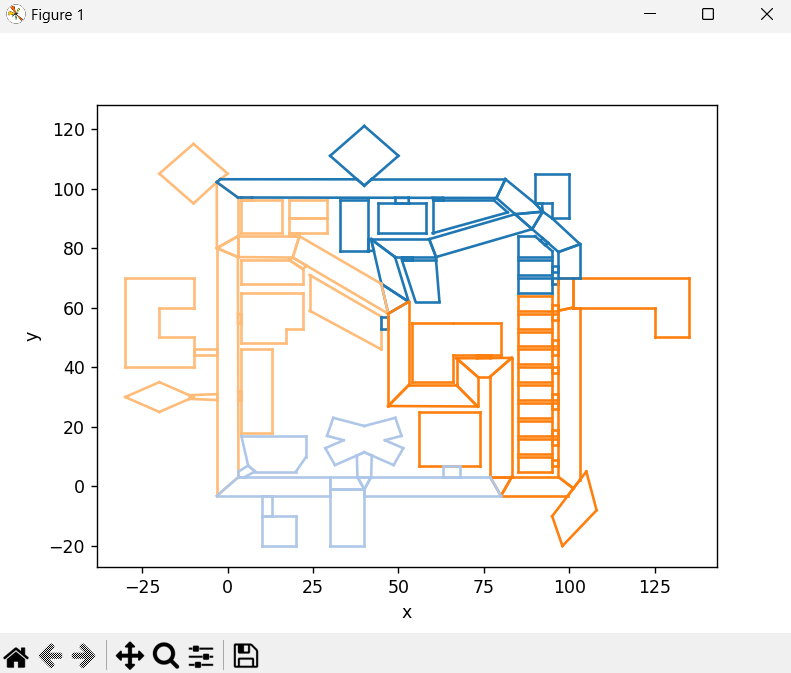
本資料で開発するモジュールは下の画像のように、
k-means++アルゴリズムによって地図上のオブジェクトをエージェント数分の区画に分けます。
Hungarian アルゴリズムによってそれらの区画とエージェントを (間の距離の総和が最も小さくなるように)1 対 1 で結びつけます。
クラスタリングモジュールの実装#
注釈
以降の作業では、カレントディレクトリがプロジェクトのルートディレクトリであることを前提としています。
まず、クラスタリングモジュールを記述するためのファイルを作成します。
mkdir -p src/<your_team_name>/module/algorithm
touch src/<your_team_name>/module/algorithm/k_means_pp_clustering.py
次に、クラスタリングモジュールの実装を行います。 以下のコードを k_means_pp_clustering.py に記述してください。
import numpy as np
from adf_core_python.core.agent.develop.develop_data import DevelopData
from adf_core_python.core.agent.info.agent_info import AgentInfo
from adf_core_python.core.agent.info.scenario_info import ScenarioInfo, ScenarioInfoKeys
from adf_core_python.core.agent.info.world_info import WorldInfo
from adf_core_python.core.agent.module.module_manager import ModuleManager
from adf_core_python.core.component.module.algorithm.clustering import Clustering
from adf_core_python.core.logger.logger import get_logger
from rcrscore.entities import (
AmbulanceCenter,
Building,
Entity,
EntityID,
FireStation,
GasStation,
Hydrant,
PoliceOffice,
Refuge,
Road,
)
from rcrscore.urn import EntityURN
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
# クラスタリングのシード値
SEED = 42
class KMeansPPClustering(Clustering):
def __init__(
self,
agent_info: AgentInfo,
world_info: WorldInfo,
scenario_info: ScenarioInfo,
module_manager: ModuleManager,
develop_data: DevelopData,
) -> None:
super().__init__(
agent_info, world_info, scenario_info, module_manager, develop_data
)
# ロガーの取得
self._logger = get_logger(f"{self.__class__.__name__}")
# クラスター数の設定
self._cluster_number: int = 1
me = agent_info.get_myself()
if not me:
self._logger.error("Myself entity is None.")
return
match me.get_urn():
# エージェントのクラスに応じてクラスター数を設定
case EntityURN.AMBULANCE_TEAM:
self._cluster_number = scenario_info.get_value(
ScenarioInfoKeys.SCENARIO_AGENTS_AT,
1,
)
case EntityURN.POLICE_FORCE:
self._cluster_number = scenario_info.get_value(
ScenarioInfoKeys.SCENARIO_AGENTS_PF,
1,
)
case EntityURN.FIRE_BRIGADE:
self._cluster_number = scenario_info.get_value(
ScenarioInfoKeys.SCENARIO_AGENTS_FB,
1,
)
# 自分と同じクラスのエージェントのリストを取得
self._agents: list[Entity] = world_info.get_entities_of_types(
[
me.__class__,
]
)
# クラスタリング結果を保持する変数
self._cluster_entities: list[list[Entity]] = []
# クラスタリング対象のエンティティのリストを取得
self._entities: list[Entity] = world_info.get_entities_of_types(
[
AmbulanceCenter,
FireStation,
GasStation,
Hydrant,
PoliceOffice,
Refuge,
Road,
Building,
]
)
def calculate(self) -> Clustering:
return self
def get_cluster_number(self) -> int:
"""
クラスター数を取得する
Returns
-------
int
クラスター数
"""
return self._cluster_number
def get_cluster_index(self, entity_id: EntityID) -> int:
"""
エージェントに割り当てられたクラスターのインデックスを取得する
Parameters
----------
entity_id : EntityID
エージェントのID
Returns
-------
int
クラスターのインデックス
"""
return self._agent_cluster_indices.get(entity_id, 0)
def get_cluster_entities(self, cluster_index: int) -> list[Entity]:
"""
クラスターのエンティティのリストを取得する
Parameters
----------
cluster_index : int
クラスターのインデックス
Returns
-------
list[Entity]
クラスターのエンティティのリスト
"""
if cluster_index >= len(self._cluster_entities):
return []
return self._cluster_entities[cluster_index]
def get_cluster_entity_ids(self, cluster_index: int) -> list[EntityID]:
"""
クラスターのエンティティのIDのリストを取得する
Parameters
----------
cluster_index : int
クラスターのインデックス
Returns
-------
list[EntityID]
クラスターのエンティティのIDのリスト
"""
if cluster_index >= len(self._cluster_entities):
return []
return [
entity.get_entity_id() for entity in self._cluster_entities[cluster_index]
]
def prepare(self) -> Clustering:
"""
エージェントの起動時に一回のみ実行される処理
"""
super().prepare()
if self.get_count_prepare() > 1:
return self
# クラスタリングを実行
kmeans_pp = self._perform_kmeans_pp(self._entities, self._cluster_number)
# クラスタリング結果を保持
self._cluster_entities = [[] for _ in range(self._cluster_number)]
for entity, cluster_index in zip(self._entities, kmeans_pp.labels_):
self._cluster_entities[cluster_index].append(entity)
# エージェントとクラスターのエンティティの距離を計算し、最も全体の合計の距離が短くなるようにエージェントとクラスターを対応付ける
agent_cluster_indices = self._agent_cluster_assignment(
self._agents, kmeans_pp.cluster_centers_
)
# エージェントとクラスターの対応付け結果を保持
self._agent_cluster_indices = {
entity.get_entity_id(): cluster_index
for entity, cluster_index in zip(self._agents, agent_cluster_indices)
}
# デバッグ用のログ出力
self._logger.info(
f"Clustered entities: {[[entity.get_entity_id().get_value() for entity in cluster] for cluster in self._cluster_entities]}"
)
self._logger.info(
f"Agent cluster indices: {[([e.get_x(), e.get_y()] if (e is not None and e.get_x() is not None and e.get_y() is not None) else [None, None], int(cluster_index)) for entity_id, cluster_index in self._agent_cluster_indices.items() for e in (self._world_info.get_entity(entity_id),)]}"
)
return self
def _perform_kmeans_pp(self, entities: list[Entity], n_clusters: int = 1) -> KMeans:
"""
K-means++法によるクラスタリングを実行する
Parameters
----------
entities : list[Entity]
クラスタリング対象のエンティティのリスト
n_clusters : int, optional
クラスター数, by default 1
Returns
-------
KMeans
クラスタリング結果
"""
entity_positions: np.ndarray = np.array(
[
[entity.get_x(), entity.get_y()]
for entity in entities
if entity.get_x() is not None and entity.get_y() is not None
]
)
entity_positions = entity_positions.reshape(-1, 2)
kmeans_pp = KMeans(
n_clusters=n_clusters,
init="k-means++",
random_state=SEED,
)
kmeans_pp.fit(entity_positions)
return kmeans_pp
def _agent_cluster_assignment(
self, agents: list[Entity], cluster_positions: np.ndarray
) -> np.ndarray:
"""
エージェントとクラスターの対応付けを行う
Parameters
----------
agents : list[Entity]
エージェントのリスト
cluster_positions : np.ndarray
クラスターの位置のリスト
Returns
-------
np.ndarray
エージェントとクラスターの対応付け結果
"""
# エージェントの位置のリストを取得
agent_positions = np.array(
[
[agent.get_x(), agent.get_y()]
for agent in agents
if agent.get_x() is not None and agent.get_y() is not None
]
)
# エージェントとクラスターの距離行列を計算
agent_positions = agent_positions.reshape(-1, 2)
cost_matrix = np.linalg.norm(
agent_positions[:, np.newaxis] - cluster_positions, axis=2
)
# ハンガリアンアルゴリズムによりエージェントとクラスターの対応付けを行う
_, col_ind = linear_sum_assignment(cost_matrix)
return col_ind
k-means++の実装は、scikit-learn のKMeansクラスを使用しています。KMeansクラスは、n_clustersで指定したクラスター数によって地図上のオブジェクトをクラスタリングします。クラスタリング結果は、labels_属性に格納されます。また、cluster_centers_属性には各クラスターの中心座標が格納されます。
hungarian アルゴリズムの実装は、scipy のlinear_sum_assignment関数を使用しています。linear_sum_assignment関数は、コスト行列を引数として受け取り、最適な割り当てを行います。
次に、作成したモジュールを登録します。config/module.yaml を以下のように編集してください。
SampleSearch:
PathPlanning: adf_core_python.implement.module.algorithm.a_star_path_planning.AStarPathPlanning
Clustering: src.<your_team_name>.module.algorithm.k_means_pp_clustering.KMeansPPClustering
SampleHumanDetector:
Clustering: src.<your_team_name>.module.algorithm.k_means_pp_clustering.KMeansPPClustering
ターミナルを 2 つ起動します。
片方のターミナルを開き、シミュレーションサーバーを以下のコマンドで起動します:
# Terminal A
cd WORKING_DIR/rcrs-server/scripts
./start-comprun.sh -m ../maps/tutorial_ambulance_team_only/map -c ../maps/tutorial_ambulance_team_only/config
その後、別のターミナルを開き、エージェントを起動します:
# Terminal B
cd WORKING_DIR/<your_team_name>
python main.py
エージェントが起動すると、標準出力にクラスタリング結果が表示されます。
[info ] Clustered entities: [[257, 259, 262, 263, 270, 278, 280, 297, 336, 913, 914, 915, 916, 917, 918, 919, 933, 941, 942, 943, 944, 945, 946, 947, 974, 250, 253], [349, 896, 899, 902, 934, 960, 968, 969, 970, 971, 248, 251], [258, 266, 268, 269, 274, 275, 279, 920, 921, 922, 923, 924, 925, 926, 927, 928, 929, 932, 948, 949, 950, 951, 952, 953, 954, 955, 956, 957, 958, 959, 975, 976, 254, 255], [256, 271, 273, 281, 296, 298, 314, 330, 903, 904, 905, 910, 911, 912, 935, 936, 937, 938, 939, 940, 247, 249]] [KMeansPPClustering]
[info ] Agent cluster indices: [([89544, 19925], 1), ([69989, 120063], 0), ([130029, 50380], 2), ([29898, 59056], 3)] [KMeansPPClustering]
このままだと、クラスタリング結果がわかりにくいので、クラスタリング結果を地図上に表示してみましょう。
クラスターの可視化用スクリプトをダウンロードして解凍し、中のmain.pyの以下の部分に
# クラスタリング結果
clusters = []
出力のClustered entities: の後ろの部分の配列をコピーして貼り付けてください。
例
# クラスタリング結果
clusters = [[257, 259, 262, 263, 270, 278, 280, 297, 336, 913, 914, 915, 916, 917, 918, 919, 933, 941, 942, 943, 944, 945, 946, 947, 974, 250, 253], [349, 896, 899, 902, 934, 960, 968, 969, 970, 971, 248, 251], [258, 266, 268, 269, 274, 275, 279, 920, 921, 922, 923, 924, 925, 926, 927, 928, 929, 932, 948, 949, 950, 951, 952, 953, 954, 955, 956, 957, 958, 959, 975, 976, 254, 255], [256, 271, 273, 281, 296, 298, 314, 330, 903, 904, 905, 910, 911, 912, 935, 936, 937, 938, 939, 940, 247, 249]]
貼り付けたら、以下のコマンドを実行してください。
pip install -r requirements.txt
python main.py
以下のような画像が出力されます。